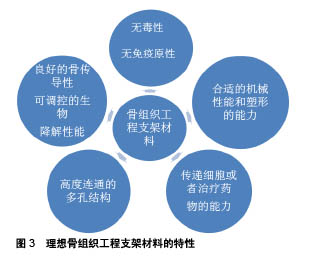
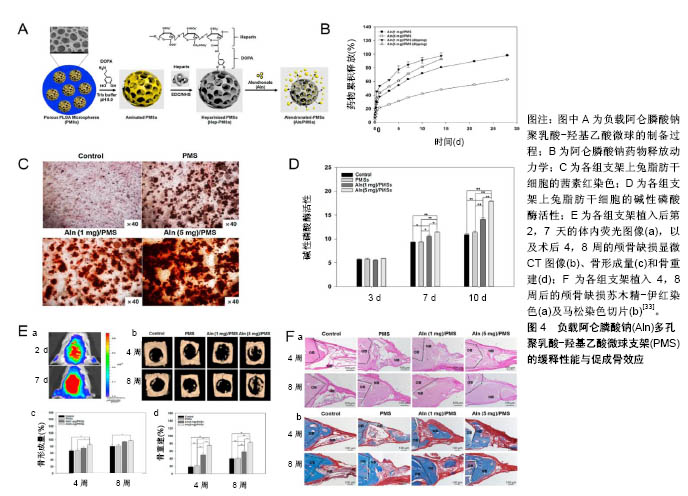
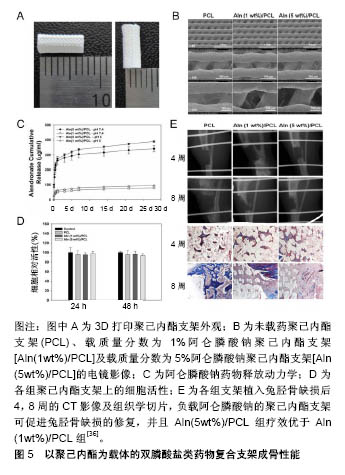
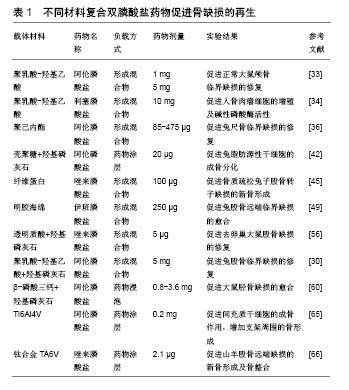
| [1] Cottrell JA, Vales FM, Schachter D, et al.Osteogenic activity of locally applied small molecule drugs in a rat femur defect model.J Biomed Biotechnol.2010;2010:597641.[2] Conners CM, Bhethanabotla VR, Gupta VK. Concentration- dependent effects of alendronate and pamidronate functionalized gold nanoparticles on osteoclast and osteoblast viability. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2017;105(1):21-29.[3] Dimitriou R, Jones E, McGonagle D, et al. Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions. BMC Med.2011;9:66.[4] Anglen KSGKMDTOMJO.Evolution of Bone Grafting: Bone Grafts and Tissue Engineering Strategies for Vascularized Bone Regeneration.Clinic Rev Bone Miner Metab.2015;13:232-244.[5] Zhu JY, Huang BL, Ding S,et al.Tethering of rhBMP-2 upon calcium phosphate cement via alendronate/heparin for localized, sustained and enhanced osteoactivity. Rsc Adv. 2017;7(33): 20281-20292.[6] Martin V, Bettencourt A. one regeneration: Biomaterials as local delivery systems with improved osteoinductive properties.Mat Sci Eng C-Mater.2018;82:363-371.[7] Liu Y, Wu G, de Groot K. Biomimetic coatings for bone tissue engineering of critical-sized defects. J R Soc Interface.2010;7 Suppl 5:S631-647.[8] Rachner TD,Khosla S,Hofbauer LC.Osteoporosis: now and the future. Lancet.2011;377(9773):1276-1287.[9] Hemmeler C, Morell S, Amsler F, et al.Screening for osteoporosis following non-vertebral fractures in patients aged 50 and older independently of gender or level of trauma energy-a Swiss trauma center approach. Arch Osteoporos.2017;12(1):38.[10] Papapoulos SE.Bisphosphonate actions: physical chemistry revisited. Bone. 2006;38(5):613-616.[11] Russell RG, Watts NB, Ebetino FH, et al.Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: similarities and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy. Osteoporos Int.2008;19(6):733-759.[12] Tarafder S, Bose S. Polycaprolactone-Coated 3D Printed Tricalcium Phosphate Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: In Vitro Alendronate Release Behavior and Local Delivery Effect on In Vivo Osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2014;6(13): 9955-9965.[13] Ossipov DA. Bisphosphonate-modified biomaterials for drug delivery and bone tissue engineering. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12(9): 1443-1458.[14] Cui P, Liu H, Sun J, et al.Zoledronate promotes bone formation by blocking osteocyte-osteoblast communication during bone defect healing. Histol Histopathol.2018;33(1):89-99.[15] Tanaka T, Saito M, Chazono M, et al.Effects of alendronate on bone formation and osteoclastic resorption after implantation of beta-tricalcium phosphate. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(2): 469-474.[16] Dutra BC, Oliveira A, Oliveira PAD, et al.Effect of 1% sodium alendronate in the non-surgical treatment of periodontal intraosseous defects: a 6-month clinical trial. J Appl Oral Sci. 2017;25(3):310-317.[17] Hu X, Neoh KG, Shi Z, et al.An in vitro assessment of fibroblast and osteoblast response to alendronate-modified titanium and the potential for decreasing fibrous encapsulation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013; 19(17-18):1919-1930.[18] Hong C, Quach A, Lin L, et al.Local vs. systemic administration of bisphosphonates in rat cleft bone graft: A comparative study.PloS One.2018;13(1):e0190901.[19] Toker H, Ozdemir H, Ozer H, et al.A comparative evaluation of the systemic and local alendronate treatment in synthetic bone graft: a histologic and histomorphometric study in a rat calvarial defect model Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;114(5): S146-S52.[20] Patel V, Graves L, Lukert B.Pelvic fractures associated with long-term bisphosphonate therapy - case report. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.2013;13(2):251-254.[21] Franceschetti P, Bondanelli M, Caruso G, et al.Risk factors for development of atypical femoral fractures in patients on long-term oral bisphosphonate therapy.Bone.2013;56(2):426-431.[22] Whyte MP, McAlister WH, Novack DV, et al. Bisphosphonate- induced osteopetrosis: Novel bone modeling defects, metaphyseal osteopenia, and osteosclerosis fractures after drug exposure ceases. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(10): 1698-107.[23] Toker H, Ozdemir H, Ozer H, et al. Alendronate enhances osseous healing in a rat calvarial defect model.Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57(11): 1545-1550.[24] 金灿,陈振琦.应用3D打印技术制作组织工程支架:修复骨缺损的研究回顾[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(10):1611-1616.[25] Li YH, Wang ZD, Wang W,et al.The biocompatibility of calcium phosphate cements containing alendronate-loaded PLGA microparticles invitro.Exp Biol Med.2015;240(11):1465-1471.[26] Shrivats AR, McDermott MC, Hollinger JO.Bone tissue engineering: state of the union. Drug Discov Today. 2014;19(6): 781-786.[27] Chen J, Luo Y, Hong L, et al.Synthesis, characterization and osteoconductivity properties of bone fillers based on alendronate-loaded poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/hydroxyapatite microspheres. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2011;22(3):547-555.[28] Cartmell S. Controlled release scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Pharm Sci.2009;98(2):430-441.[29] Wang CZ, Chen SM, Chen CH, et al.The effect of the local delivery of alendronate on human adipose-derived stem cell-based bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2010;31(33):8674-8683.[30] Shi XT, Ren L, Tian M, et al.In vivo and in vitro osteogenesis of stem cells induced by controlled release of drugs from microspherical scaffolds. J Mater Chem.2010;20(41):9140-9148.[31] Posadowska U, Parizek M, Filova E, et al.Injectable nanoparticle-loaded hydrogel system for local delivery of sodium alendronate.Int J Pharmaceut.2015;485(1-2):31-40.[32] Limirio PHJO, Rocha FS, Batista JD, et al.The Effect of Local Delivery Doxycycline and Alendronate on Bone Repair. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2016;17(4):872-877.[33] Lee JY, Kim SE, Yun YP, et al. Osteogenesis and new bone formation of alendronate-immobilized porous PLGA microspheres in a rat calvarial defect model.J Ind Eng Chem.2017;52:277-286.[34] Elkasabgy NA, Mahmoud AA, Shamma RN.Determination of cytocompatibility and osteogenesis properties of in situ forming collagen-based scaffolds loaded with bone synthesizing drug for bone tissue engineering. Int J Polym Mater Po. 2018;67(8): 494-500.[35] Wang YH, Rajalakshmanan E, Wang CK, et al. PLGA-linked alendronate enhances bone repair in diaphysis defect model. J Tissue Eng Regen M. 2017;11(9):2603-2612.[36] Kim SE, Yun YP, Shim KS, et al.3D printed alendronate-releasing poly(caprolactone) porous scaffolds enhance osteogenic differentiation and bone formation in rat tibial defects.Biomed Mater. 2016;11(5):055005.[37] Song JQ, Zhu GL, Wang L,et al.Assembling of electrospun meshes into three-dimensional porous scaffolds for bone repair. Biofabrication. 2017;9(1):015018.[38] Valente FL,Reis ECC,Sepulveda RV,et al.Hydroxyapatite, polycaprolactone and alendronate composites for bone regeneration in rabbits' olecranon: histological features. Arq Bras Med Vet Zoo. 2016;68(2):543-547.[39] Dash M, Chiellini F, Ottenbrite RM, et al.Chitosan-A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2011;36(8):981-1014.[40] Wu HW, Lei PF, Liu GY, et al.Reconstruction of Large-scale Defects with a Novel Hybrid Scaffold Made from Poly(L-lactic acid)/Nanohydroxyapatite/Alendronate-loaded Chitosan Microsphere: in vitro and in vivo Studies. Sci Rep.2017;7(1):359.[41] Ding CC, Teng SH, Pan H.In-situ generation of chitosan/ hydroxyapatite composite microspheres for biomedical application. Mater Lett.2012;79:72-74.[42] Wu H, Xu Y, Liu G,et al.Emulsion cross-linked chitosan/ nanohydroxyapatite microspheres for controlled release of alendronate. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(12):2649-2658.[43] Janmey PA, Winer JP, Weisel JW. Fibrin gels and their clinical and bioengineering applications. J R Soc Interface. 2009;6(30):1-10.[44] Kim BS, Shkembi F, Lee J.In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Commercially Available Fibrin Gel as a Carrier of Alendronate for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:6434169.[45] Jing D, Hao XG, Xu F, et al.Effects of local delivery of BMP2, zoledronate and their combination on bone microarchitecture, biomechanics and bone turnover in osteoporotic rabbits.Sci Rep. 2016;6:28537. [46] Kanoriya D, Pradeep AR, Garg V,et al.Mandibular Degree II Furcation Defects Treatment With Platelet-Rich Fibrin and 1% Alendronate Gel Combination: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.J Periodontol.2017;88(3):250-258.[47] Zhang YR, Hu Y, Luo Z,et al.Simultaneous delivery of BMP-2 factor and anti-osteoporotic drugs using hyaluronan-assembled nanocomposite for synergistic regulation on the behaviors of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2015;26(5):290-310.[48] He YC, Zhu T, Liu L,et al.Modifying collagen with alendronate sodium for bone regeneration applications.Rsc Adv. 2018;8(30): 16762-16772.[49] Yang ZY, Chen W, Xia ZD, et al.Local Application of Ibandronate/ Gelatin Sponge Improves Osteotomy Healing in Rabbits. PloS One. 2015;10(5):e0125807.[50] Hur W, Park M, Lee JY, et al. Bioabsorbable bone plates enabled with local, sustained delivery of alendronate for bone regeneration. J Control Release.2016;222:97-106.[51] Cattalini JP,Roether J,Hoppe A,et al.Nanocomposite scaffolds with tunable mechanical and degradation capabilities: co-delivery of bioactive agents for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2016;11(6):065003.[52] Huang J, Lin YW, Fu XW, et al.Development of nano-sized hydroxyapatite reinforced composites for tissue engineering scaffolds. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2007;18(11):2151-2157.[53] Yang H, Gao H, Wang Y.Hollow hydroxyapatite microsphere: a promising carrier for bone tissue engineering. J Microencapsul. 2016:1-6.[54] Boanini E, Torricelli P, Gazzano M, et al. Alendronate- hydroxyapatite nanocomposites and their interaction with osteoclasts and osteoblast-like cells. Biomaterials. 2008;29(7): 790-796.[55] Canettieri ACV, Colombo CED, Chin CM, et al.Femur bone repair in ovariectomized rats under the local action of alendronate, hydroxyapatite and the association of alendronate and hydroxyapatite. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009;90(5):520-526.[56] Kettenberger U,Luginbuehl V, Procter P,et al.In vitro and in vivo investigation of bisphosphonate-loaded hydroxyapatite particles for peri-implant bone augmentation. J Tissue Eng Regen M. 2017; 11(7): 1974-1985.[57] Ni M, Li G, Tang PF, et al. rhBMP-2 not alendronate combined with HA-TCP biomaterial and distraction osteogenesis enhance bone formation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(11):1469-1476.[58] Tarafder S, Bose S.Polycaprolactone-coated 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: in vitro alendronate release behavior and local delivery effect on in vivo osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(13):9955-9965.[59] Naineni R, Ravi V, Subbaraya DK, et al.Effect of Alendronate with beta - TCP Bone Substitute in Surgical Therapy of Periodontal Intra-Osseous Defects: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J Clin Diagn Res.2016;10(8):ZC113-117.[60] Park KW, Yun YP, Kim SE, et al.The Effect of Alendronate Loaded Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Scaffolds on Bone Regeneration in a Rat Tibial Defect Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):26738-26753.[61] Villaca JC, da Silva LCRP, de Alexandria AK, et al.Development and characterization of clay-polymer nanocomposite membranes containing sodium alendronate with osteogenic activity.Appl Clay Sci. 2017;146:475-486.[62] Kim SE, Yun YP, Park K,et al.The effects of functionalized titanium with alendronate and bone morphogenic protein-2 for improving osteoblast activity. Tissue Eng Regen Med.2013;10(6):353-361.[63] Kapat K, Srivas PK, Rameshbabu AP, et al.Influence of Porosity and Pore-Size Distribution in Ti6Al4 V Foam on Physicomechanical Properties, Osteogenesis, and Quantitative Validation of Bone Ingrowth by Micro-Computed Tomography. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(45):39235-39248.[64] Bosco R, Iafisco M, Tampieri A, et al.Hydroxyapatite nanocrystals functionalized with alendronate as bioactive components for bone implant coatings to decrease osteoclastic activity.Appl Surf Sci. 2015; 328:516-524.[65] Rojo L, Gharibi B, McLister R,et al.Self-assembled monolayers of alendronate on Ti6Al4V alloy surfaces enhance osteogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells.Sci Rep. 2016;6:30548.[66] Stadelmann VA, Gauthier O, Terrier A, et al.Implants Delivering Bisphosphonate Locally Increase Periprosthetic Bone Density in an Osteoporotic Sheep Model. A Pilot Study.Eur Cells Mater. 2008;16: 10-16.[67] Park CG, Park M, Kim BH, et al.Pattern-Coated Titanium Bone Fixation Plate for Dual Delivery of Vancomycin and Alendronate. Macromol Res. 2017;25(7):756-762.[68] Levine B, Della Valle CJ, Jacobs JJ.Applications of porous tantalum in total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006; 14(12):646-655.[69] Garbuz DS, Hu Y, Kim WY,et al.Enhanced gap filling and osteoconduction associated with alendronate-calcium phosphate- coated porous tantalum. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(5): 1090-1100.[70] Wei PB, Wang B, Lu X, et al.Bio-inspired immobilization of strontium substituted hydroxyapatite nanocrystals and alendronate on the surface of AZ31 magnesium alloy for osteoporotic fracture repair. Surf Coat Tech. 2017;313:381-390. |
.jpg)


.jpg)